價格:免費
檔案大小:87.5 MB
版本需求:系統需求:iOS 10.0 或以後版本。相容裝置:iPhone、iPad、iPod touch。
支援語言:英語

The key metric for high yields in indoor agriculture.
Vapor pressure deficit (VPD) is the difference between the amount of water in the air and the maximum amount of water the air can hold for a given temperature (saturation). It is usually measured in kilopascals (kPa) or bars. A low VPD is indicative of high moisture content in the air and a high VPD is indicative of low moisture content.
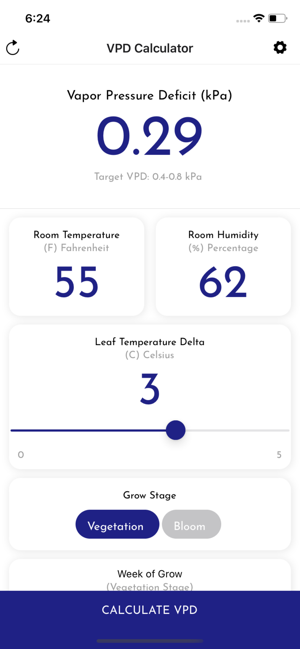
The surface of leaves is commonly assumed to be saturated with water. Plant stomatal opening is directly related to VPD. If VPD is too high, stomata will close to conserve water. If it’s too low, stomata may be fully open, but evapotranspiration will be slow and nutrient uptake will be impacted. Both conditions can cause wilting, leaf tip burn and other crop maladies. When VPD is managed correctly, plants will transpire freely, move nutrients readily to cells and maximize CO2 uptake.
